 项目结构
项目结构
# 3.1 项目结构
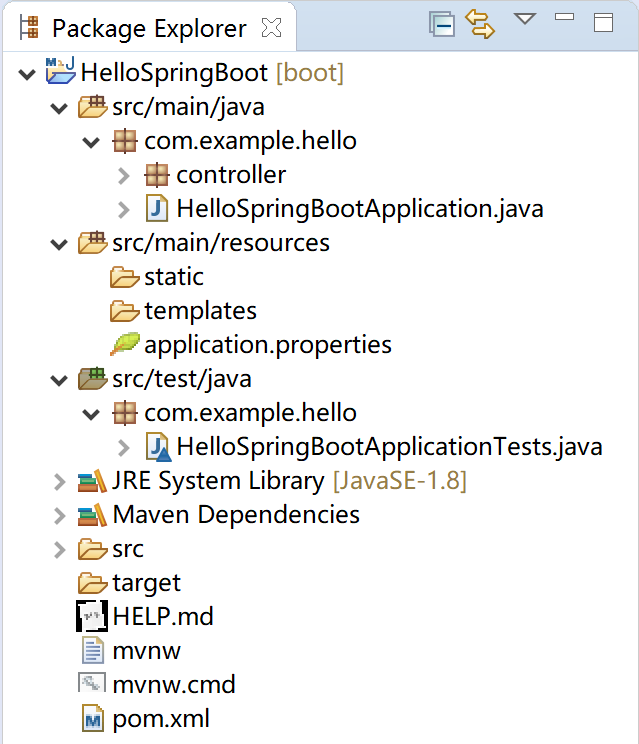
Spring 官方为我们生成的项目,都具有固定的项目结构。下面,我们以上一章提供的“Hello Spring Boot”项目为例,来介绍 Spring Boot 的项目结构。
# 3.1.1 Maven 配置文件
pom.xml 文件,maven 项目的配置依赖管理文件。其中包含了 Spring Boot 版本、各种 starter 和spring-boot-maven-plugin 插件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>hello</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>HelloSpringBoot</name>
<description>My First Spring Boot Project.</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
- spring-boot-starter-parent:是 Spring Boot 的版本仲裁中心,其指定了 Spring Boot 的版本;
- starter 启动器:Spring Boot 的各种模块依赖,基于自动配置,为我们做了大量的配置依赖工作;
- spring-boot-maven-plugin 插件: 能够以 Maven 的方式为应用提供 Spring Boot 的支持,即为 Spring Boot 应用提供了执行 Maven 操作的可能。 能够将 Spring Boot 应用打包为可执行的 jar 或 war 文件,然后以通常的方式运行 Spring Boot 应用。
这里特别说明一下 spring-boot-maven-plugin 提供的 5 个 Maven Goals:
- spring-boot:repackage,默认 goal。在 mvn package 之后,再次打包可执行的 jar/war,同时保留 mvn package 生成的 jar/war 为 .origin;
- spring-boot:run,运行 Spring Boot 应用;
- spring-boot:start,在 mvn integration-test 阶段,进行 Spring Boot 应用生命周期的管理;
- spring-boot:stop,在 mvn integration-test 阶段,进行 Spring Boot 应用生命周期的管理;
- spring-boot:build-info,生成 Actuator 使用的构建信息文件 build-info.properties。
# 3.1.2 src/main/java
代码主目录,Spring Boot 的启动类就在这里。例如,com.example.hello.HelloSpringBootApplication。
启动类管理了其下的各个 package 的默认扫描,例如扫描其下 package 中的 Controller。
根据项目开发规范,一般而言,其实体类(entity) 、数据访问类(Dao) 、服务类(Service) 、前端控制器(Controller) 、常量接口类(constant) 和一些工具类(utils) 都应该放置在这里。
# 3.1.3 src/main/resources
各种资源,如配置文件 application.properties 都应该放在这里。如果你的程序使用了 MyBatis,则其 mapper 文件也应该放在这里的某个子目录下。
静态资源文件存放在 static 子目录中。如果你的 Spring Boot 应用是个前后端分离的项目,为了简化部署(只有一台服务器,服务用户人数在 50 人左右的简单应用),可以将前端 vue 的对应文件放置在这里,然后使用java -jar xxx.jar就可以运行这个程序了。
动态模板文件存放在 templates 子目录中。例如项目中的 Thymeleaf 模板文件。
# 3.1.4 src/test/java
顾名思义,这里是单元测试代码的栖身之处。
以第1章 Spring Boot介绍中的“Hello Spring”项目为例,HelloSpringBootApplicationTests这个测试类就存放在这个目录下。
package com.example.hello;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class HelloSpringBootApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() {
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
