 热部署
热部署
# 11.2 Spring Boot 对热部署的支持
**spring-boot-devtools (opens new window)**是一个为开发者服务的一个模块,主要功能是监控程序的变化,然后进行自动重新启动,速度比手动停止后再启动要快,这样就可以节省出来手工操作的时间,达到提高开发效率工作效率的目的。
其实现原理主要是使用了两个类加载器(ClassLoader):
- 一个根 Class Loader 加载不会改变的类(第三方Jar包);
- 另一个称为 Restart Class Loader 的类加载器加载会更改的类,这样在有代码更改的时候,原来的 Restart Class Loader 被丢弃,重新创建一个新的 Restart Class Loader,由于需要加载的类相比较少,所以实现了较快(秒级)的重启时间。
默认情况下,当 DevTools 检测到 classpath 下有文件(Class文件、配置文件等资源)内容变更时,它会对当前 Spring Boot 应用进行重新启动。
这种设计可以让程序快速的进行重启,因为这个时候第三方 jar 包中的资源已经在第一次启动的时候进行加载了,自动重启的时候就不需要加载它们了。在开发的时候,希望改动后立马生效的通常也是应用中自己定义的 Class 及其它资源。
在日常开发中,有些时候,我们会在修改了一组文件后才测试,也就是说我们不想在改变 Class Path 路径下的任何文件后立马就进行自动重启,而是希望在更改了很多文件后,在更改了一个特殊的文件后才触发自动重启。针对这种情况,可以通过 spring.devtools.restart.trigger-file 属性指定触发自动重启的文件,这样当该文件的内容发生了变更后就会触发自动重启。比如下面的配置就表示当更改了 application.properties 文件的内容时将触发自动重启。
spring.devtools.restart.trigger-file=application.properties
通过查看DevToolsPropertyDefaultsPostProcessor类,可以了解到 devtools 为方便开发提供的默认值:
private static final Map<String, Object> PROPERTIES;
static {
Map<String, Object> properties = new HashMap<>();
properties.put("spring.thymeleaf.cache", "false");
properties.put("spring.freemarker.cache", "false");
properties.put("spring.groovy.template.cache", "false");
properties.put("spring.mustache.cache", "false");
properties.put("server.servlet.session.persistent", "true");
properties.put("spring.h2.console.enabled", "true");
properties.put("spring.resources.cache.period", "0");
properties.put("spring.resources.chain.cache", "false");
properties.put("spring.template.provider.cache", "false");
properties.put("spring.mvc.log-resolved-exception", "true");
properties.put("server.error.include-stacktrace", "ALWAYS");
properties.put("server.servlet.jsp.init-parameters.development", "true");
properties.put("spring.reactor.debug", "true");
PROPERTIES = Collections.unmodifiableMap(properties);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
当然,在我们的应用中,某些资源的修改其实并不需要重启服务。比如前端使用的静态资源文件,默认情况下,Spring Boot 在以下这些目录中的资源变更时,不会触发重启(但是会触发 live reload):
/META-INF/maven , /META-INF/resources , /resources , /static , /public , /templates
我们也可以手动指定不需要重启的资源,覆盖 devtools 的默认值:
spring.devtools.restart.exclude=static/**,public/**
也可以在默认值上额外添加不需要重启的资源:
spring.devtools.restart.additional-exclude = /custom-path/**
如果我们觉得 Spring Boot dev-tools 提供的重启还是不够快的话,可以尝试使用其它的基于 Reload 的技术,如收费的JRebel。
在 Spring Boot 中使用 devtools 非常方便。使用 Spring Starter 创建项目时,勾选Spring Boot DevTools启动器依赖即可。
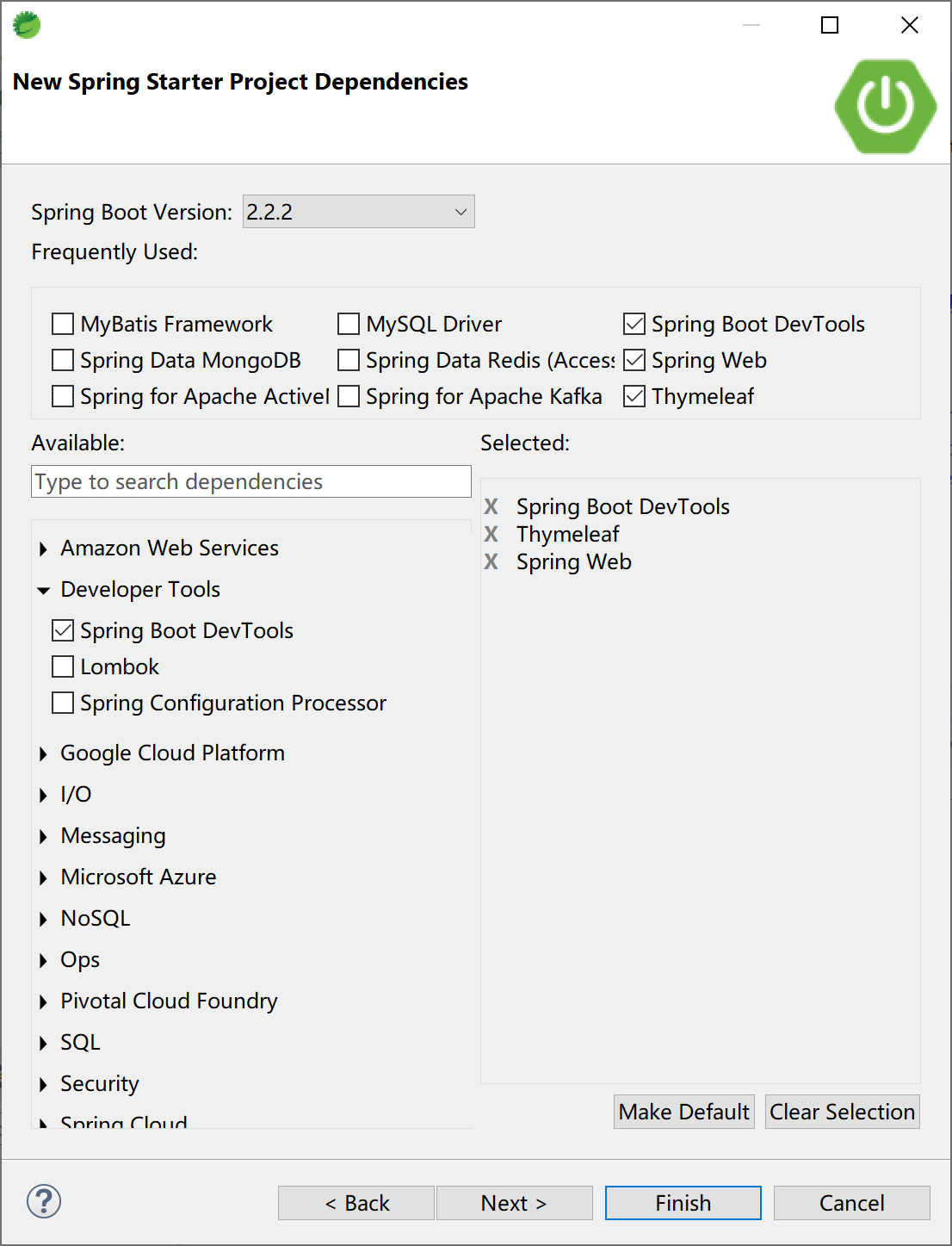
创建的初始项目 pom 文件中配置 dev-tools 的依赖为:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
6
绝大多数情况下
spring-boot-devtools只使用于开发环境,在生产环境是需要禁用的,所以Spring Starter为我们生成的项目中spring-boot-devtools通过<optional>true</optional>配置到了开发环境。
在后续开发,这个项目就具有热部署(开发过程中,Debug As启动项目后根据情况重启)的功能了。
创建一个测试用的 Controller 类。
package com.example.devtools.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/devtools/")
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String hello() {
return "Hello DevTools.";
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
以 debug 方式(在项目上右键,选择Debug As)启动项目。
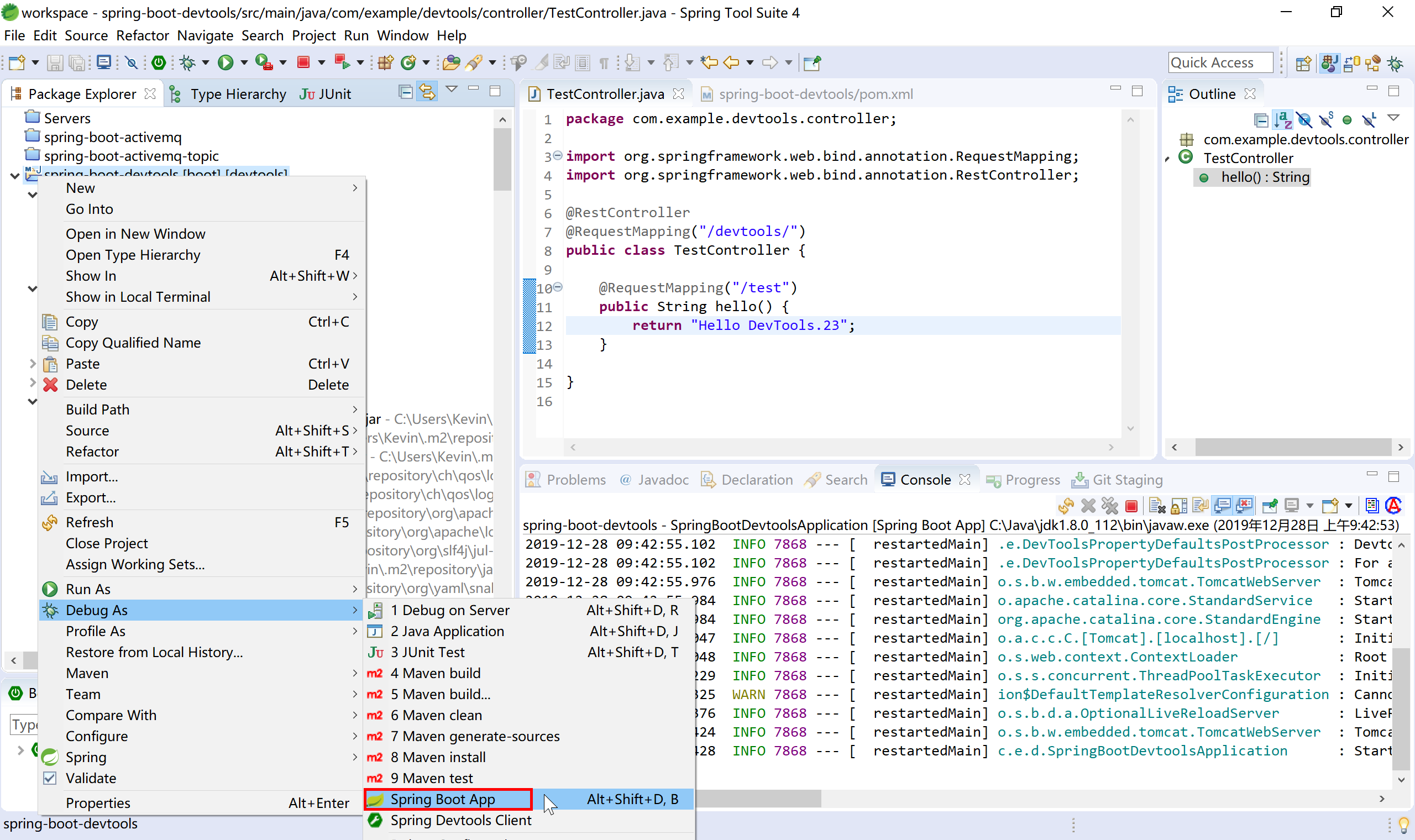
在 hello 方法中,修改返回的字符串值,使用浏览器(http://localhost:8080/devtools/test (opens new window)) 测试,可以看到在不重新启动的情况下,浏览器能够正确返回 hello 方法修改后的字符串。
本小节示例项目代码:
https://github.com/gyzhang/SpringBootCourseCode/tree/master/spring-boot-devtools (opens new window)
