 单元测试
单元测试
# 11.1 Spring Boot 中的单元测试
单元测试是指对软件中的最小可测试单元进行检查和验证,单元测试归属于白盒测试。
这个定义有点抽象,下面举几个单元测试的特性,大家感受一下:
- 一般是一个函数配几个单元测试;
- 单元测试不应该依赖外部系统;
- 单元测试运行速度很快;
- 单元测试不应该造成测试环境的脏数据;
- 单元测试可以重复运行。
单元测试使得我们可以放心修改、重构业务代码,而不用担心修改某处代码后带来的副作用。
单元测试可以帮助我们反思模块划分的合理性,如果一个单元测试写得逻辑非常复杂、或者说一个函数复杂到无法写单元测试,那就说明模块的抽象有问题。
单元测试使得系统具备更好的可维护性、具备更好的可读性。对于团队的新人来说,可以从单元测试入手阅读代码,进而熟悉系统的逻辑。
优秀的开源框架,都配有完善的单元测试套件(Test Suite),以保证代码质量。
越是底层的代码,越是被更多客户调用的代码,越应该实践 TDD(Test-Driven Development,测试驱动开发)。
测试驱动开发的基本思想就是在开发功能代码之前,先编写测试代码。也就是说在明确要开发某个功能后,首先思考如何对这个功能进行测试,并完成测试代码的编写,然后编写相关的代码满足这些测试用例。然后循环进行添加其他功能,直到完全部功能的开发。
虽然,我们日常工作中不会为每一段业务逻辑(类或方法)提供单元测试,但是针对大部分的产品级业务系统(主要工作是在某一技术基础平台上实现业务逻辑),都应该写单元测试。
大部分开发人员使用的单元测试框架都是 JUnit,这也是 Spring Boot 的选择。
# 11.1.1 使用单元测试
Spring Boot 官方文档 (opens new window),对如何进行测试进行了充分的说明。
Spring Boot provides a number of utilities and annotations to help when testing your application. Test support is provided by two modules:
spring-boot-testcontains core items, andspring-boot-test-autoconfiguresupports auto-configuration for tests.
使用 Spring Starter 创建项目时,默认就添加了spring-boot-starter-test依赖。
查看项目 pom 文件中的单元测试依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
spring-boot-starter-test启动器依赖提供如下支持库:
- JUnit 5(包括与JUnit 4向后兼容的老式引擎):Java 领域的单元测试事实标准,使用最广泛的测试支持库。
- Spring Test 和 Spring Boot Test:对 Spring Boot 应用提供集成测试支持。
- AssertJ:Java 领域常用的功能完备的断言库。
- Hamcrest:一个匹配对象的库(也称为约束或谓词)。
- Mockito:一个 Java 模拟框架,比如模拟 http 容器环境。
- JSONassert:JSON 的断言库。
- JSONPath:JSON 的 XPath 支持库。
Spring Boot 认为这些公共库在编写测试时很有用。如果这些库不适合我们的需要,也可以手动添加自己喜欢的测试依赖库。
通过查看org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starters依赖,可以看到其依赖的 JUnit 的版本信息
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId>
<version>5.5.2</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
6
打开 Spring Boot 创建的项目中的默认单元测试入口类SpringBootTestApplicationTests:
package com.example.test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringBootTestApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() {
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
在 contextLoads 方法中添加一个断言:
@Test
void contextLoads() {
int num = new Integer(6998);
assertEquals(num, 6998);
}
2
3
4
5
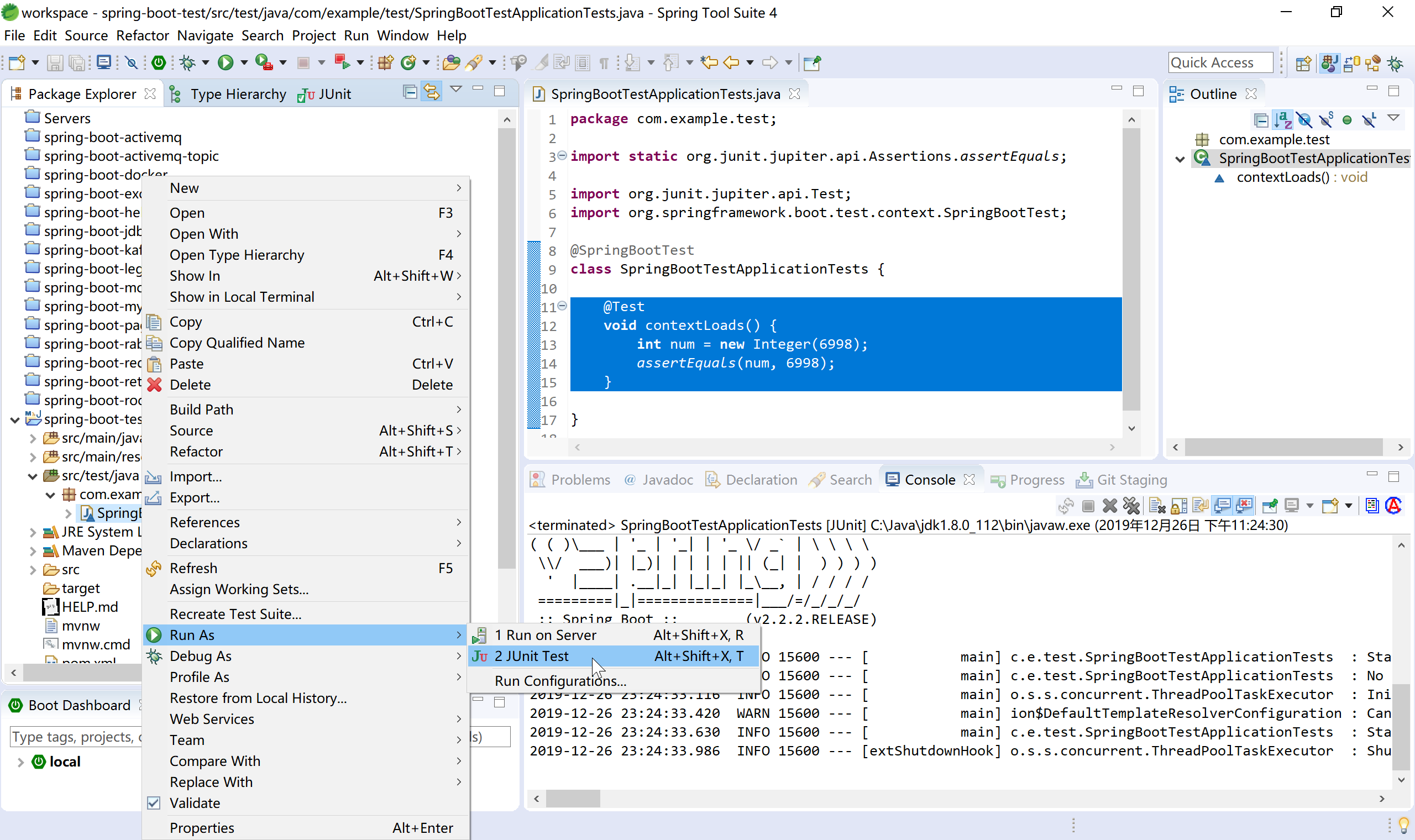
选中单元测试入口类,运行JUnit Test:
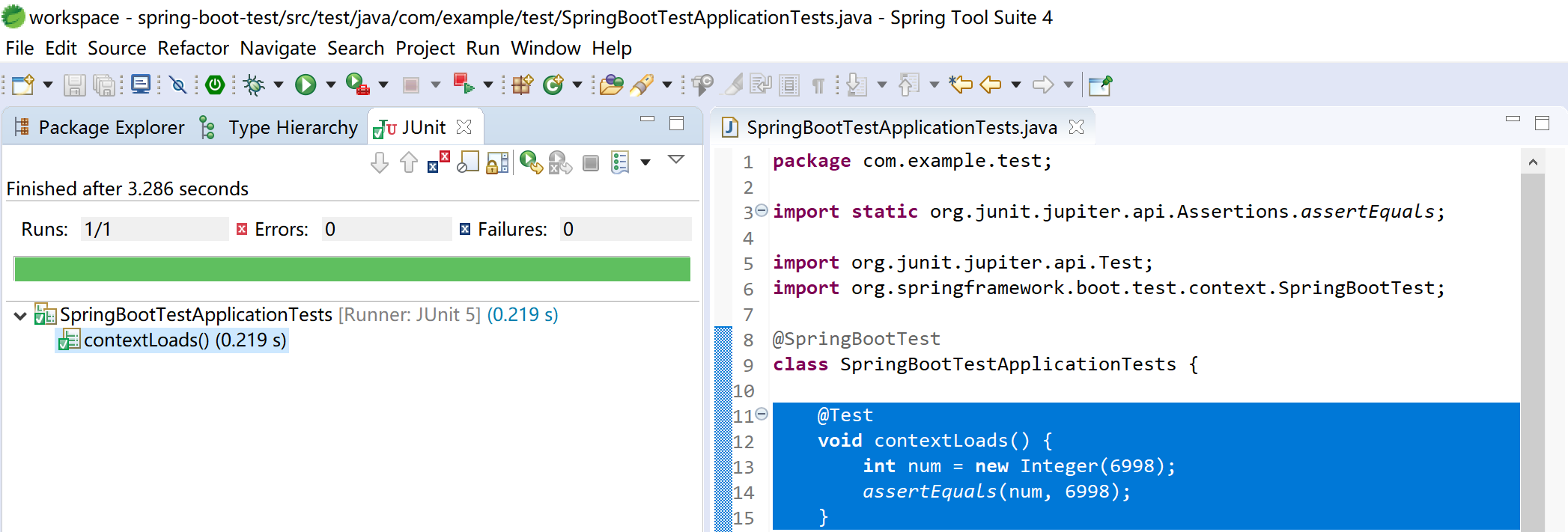
查看单元测试运行结果,如果没有错误,会出现熟悉的绿色长条。
# 11.1.2 普通后台代码测试
添加测试用的 DAO 类 TestDAO,模拟从数据库中查询数据后返回用户年龄。其业务逻辑是“kevin用户的年龄为18岁”。
package com.example.test.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class TestDAO {
//模拟从数据库访问数据后返回用户的年龄
public int getUserAge(String userId) {
int result = 0;
if (userId.equals("kevin")) {
result = 18;
} else if (userId.equals("roy")) {
result = 12;
} else {
result = 28;
}
return result;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
添加测试用服务类 TestService,使用 TestDAO 从数据库(模拟)中获取用户年龄。
package com.example.test.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.example.test.dao.TestDAO;
@Service
public class TestService {
@Autowired
TestDAO testDAO;
public int getUserAge(String userId) {
return testDAO.getUserAge(userId);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
在测试启动类中添加测试方法 testService,使用注入的 TestService 获取用户kevin的年龄,并做相等断言(年龄等于18)。
@Autowired
TestService testService;
@Test
void testService() {
int age = testService.getUserAge("kevin");
assertEquals(18, age);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
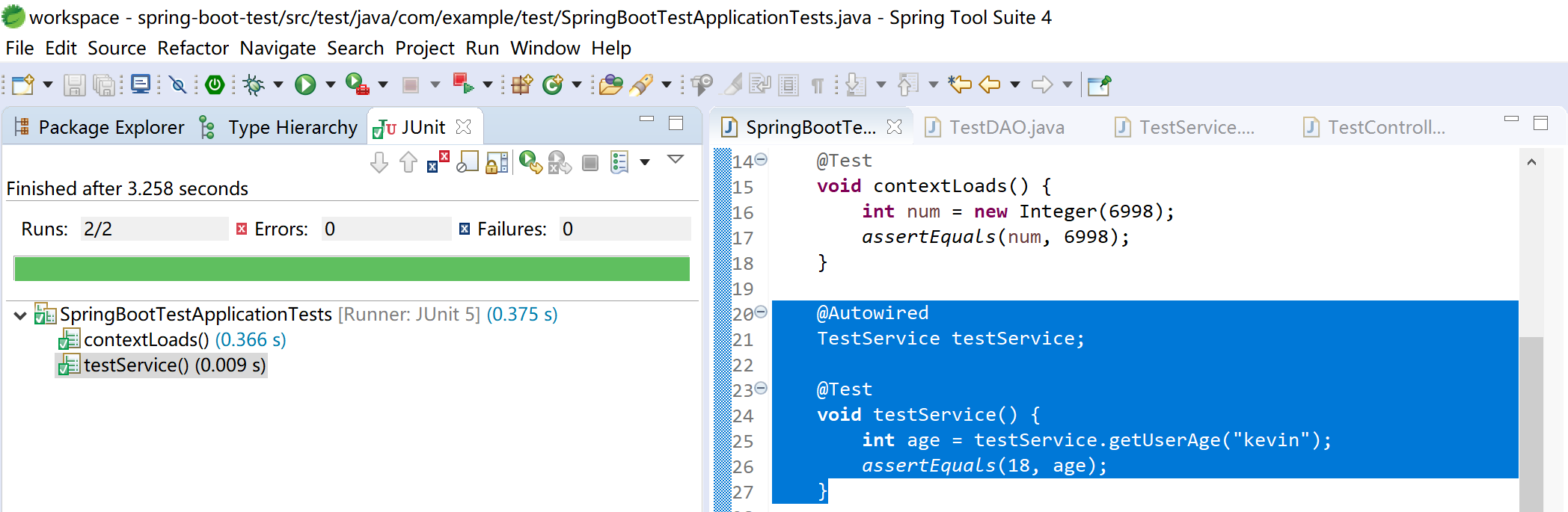
运行测试,查看测试结果。
# 11.1.3 使用 Mock 测试控制层
由于控制器层会从浏览器接收用户的输入,所以在对测试控制层进行单元测试时,需要对 Spring MVC 和 Servlet 容器进行模拟,具体的模拟类为 MockMvc。
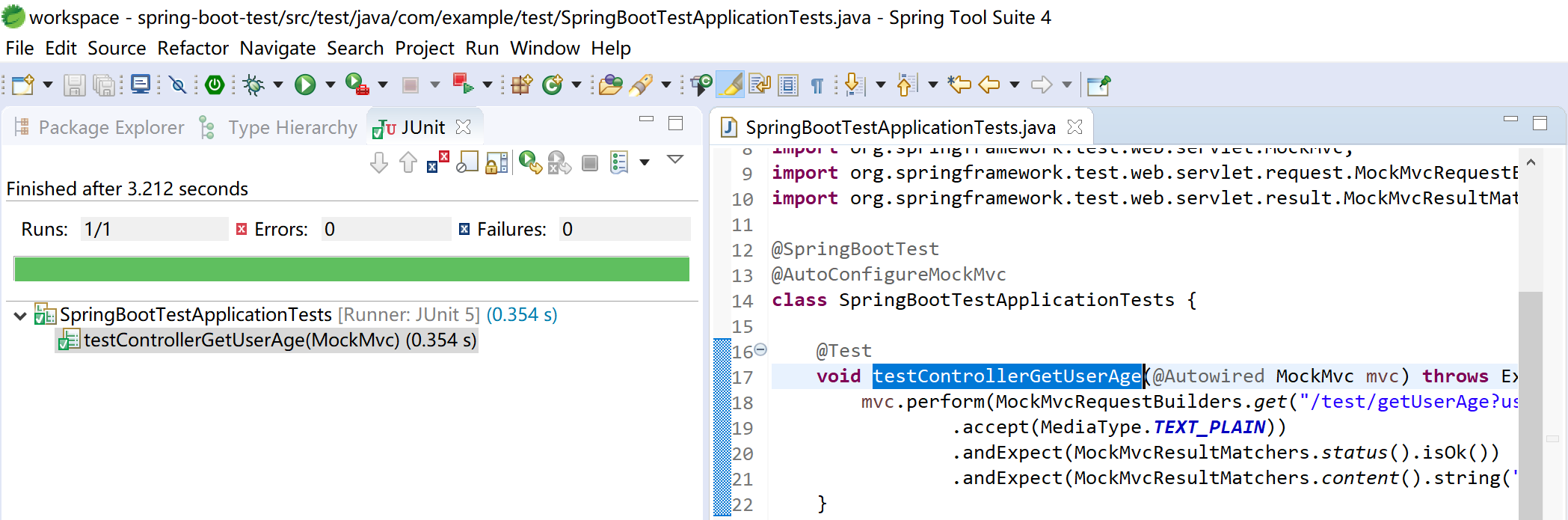
修改测试启动类,为其添加@AutoConfigureMockMvc注解,启动 MockMvc,创建 testControllerGetUserAge 测试方法,注意理解其中使用的 MockMvc.perform 方法,MockMvcRequestBuilders.get 方法,MockMvcResultMatchers.status 方法和 MockMvcResultMatchers.content 方法。
package com.example.test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers;
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
class SpringBootTestApplicationTests {
@Test
void testControllerGetUserAge(@Autowired MockMvc mvc) throws Exception {
mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/test/getUserAge?userId=kevin")
.accept(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.content().string("User[kevin]'s age is: 18."));
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
运行 JUnit Test,检查测试结果:
# 11.1.4 运行服务器后测试
有时候我们需要在一个完整运行的服务器中进行控制层的测试(模拟用户的浏览器操作行为),这个时候,我们可以使用 Spring Boot 提供的 TestRestTemplate 模板类来完成对运行中的服务器进行测试。
这个行为,已经不太像单元测试了,我个人认为有点儿像自动化测试了。
package com.example.test;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment;
import org.springframework.boot.test.web.client.TestRestTemplate;
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
class RandomPortTestRestTemplateExampleTests {
@Test
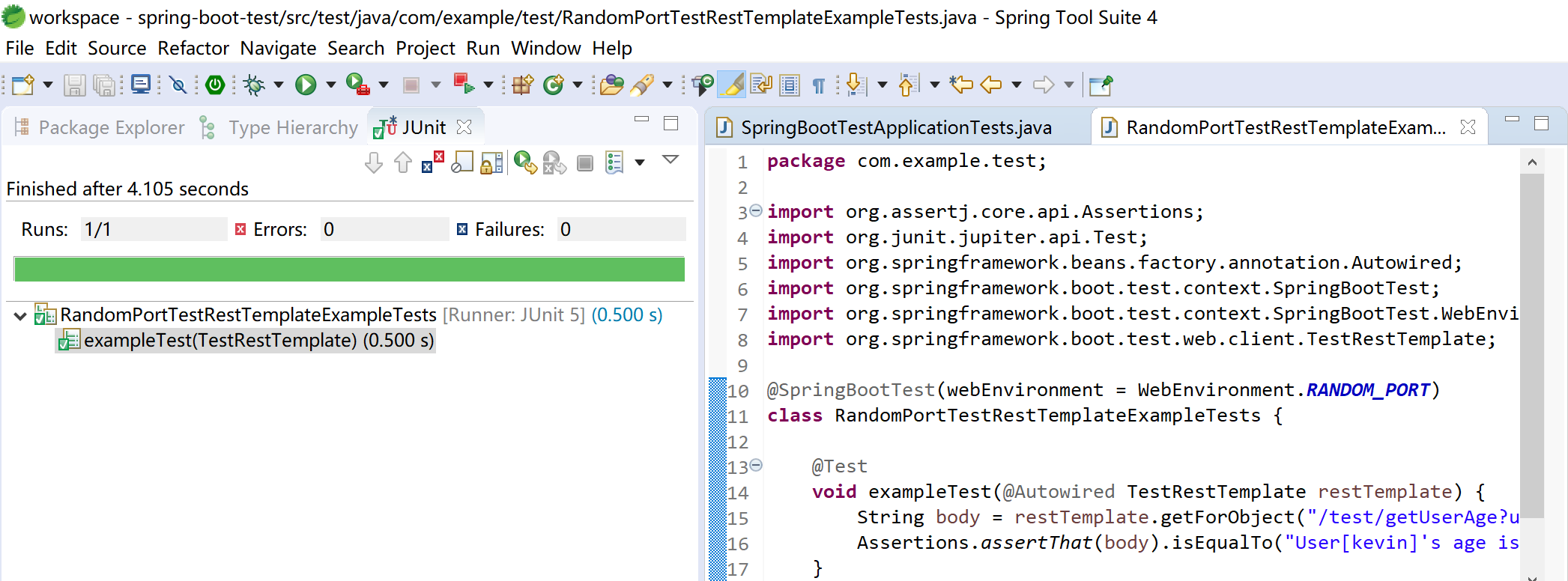
void exampleTest(@Autowired TestRestTemplate restTemplate) {
String body = restTemplate.getForObject("/test/getUserAge?userId=kevin", String.class);
Assertions.assertThat(body).isEqualTo("User[kevin]'s age is: 18.");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
运行 JUnit Test,然后查看测试结果:
本小节示例项目代码:
https://github.com/gyzhang/SpringBootCourseCode/tree/master/spring-boot-test (opens new window)
